Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a Mental Health Disorder that affects around 1% of the population. It’s characterized by intrusive thoughts and repetitive, ritualistic behaviors that have no obvious reason. Fortunately, there are ways to treat OCD and get your life back in balance. One such treatment is DBS or deep brain stimulation. In this blog post, we will explore all you need to know about DBS for OCD and how it can help you. From the basics of the procedure to its potential benefits, read on to learn everything you need to know!
Contents
What is DBS?
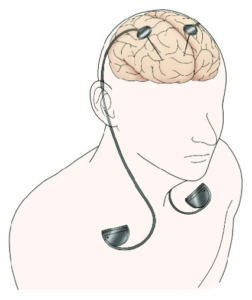
DBS or deep brain stimulation is a neurostimulation therapy that uses electrical pulses to treat a variety of conditions, including Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
DBS therapy is delivered through a surgically implanted device that sends electrical impulses to specific areas of the brain. The hope is that this will help improve the symptoms associated with these conditions.
There is currently no cure for Parkinson’s disease or any of the other conditions that can be treated with DBS, but the therapy is thought to be very effective in slowing down the progression of the disease or improving symptoms significantly.
There are a few potential side effects associated with DBS therapy, including headaches, mood swings, and sexual dysfunction. It is important to speak with your doctor about any potential risks before scheduling surgery.
What are The Benefits of DBS For OCD?
DSM-5 defines OCD as a persistent and obsessional thought or behavior that is experienced repeatedly and causes significant distress or functional impairment.
Some of the benefits of DBS for OCD include:
- Relieve Symptoms of OCD: Patients report relief from symptoms, including intrusive thoughts, repetitive behaviors, and compulsions.
- Improve Quality of Life: Individuals with OCD often have decreased quality of life due to their chronic anxiety. In some cases, DBS can improve the overall quality of life by reducing anxiety levels.
- Reduce Stress Levels: DBS has been shown to reduce stress levels in people with OCD. This may result in reduced compulsions and fewer negative thoughts.
- Promote Well-being: A healthy mind is essential for a healthy body, and DBS has been linked to promoting general well-being. Also, individuals with OCD often have a higher risk of developing other chronic medical conditions. DBS may help to improve overall health.
How Does DBS For OCD Work?

There is not one specific approach that is recommended for everyone who wants to try DBT for OCD, as the best way to achieve success will vary based on each individual’s unique situation and history. However, some core features that are often included in DBT for OCD treatments include:
1) Individualized treatment plans are important when it comes to DBT for OCD. The goal is to help each person find the exercises and approaches that work best for them, based on their personal history, diagnosis, and goals.
2) Meeting regularly with a mental health professional is essential during treatment. This allows individuals to discuss their progress and challenges, as well as receive guidance and support in implementing their treatment plan.
3) Avoidance of triggers is key when it comes to DBT for OCD. While it may be difficult at first, learning how to resist responding to intrusive thoughts and urges is essential in reducing symptoms.
4) Accepting responsibility for one’s behavior is also a key component of DBT for OCD treatments. Individuals should learn how to identify and address negative thoughts and behaviors, rather than assuming the blame for them.
What Are The Risks of DBS For OCD?
The risks of DBS for OCD are numerous and include the following:
1. Initial risks: The first and most likely risk of DBS for OCD is that it may not work as intended. This is because DBS is an invasive treatment and can lead to complications such as infection, bleeding, seizure, and even death. In addition, there is a significant risk that the electrodes will be placed in areas where they do not produce therapeutic effects (known as “undesired side effects”), which could worsen OCD symptoms.
2. Long-term risks: There are also long-term risks associated with DBS for OCD, including the possibility that the electrodes will cause additional problems elsewhere in the body (such as causing seizures), that the device will need to be replaced or upgraded over time (which could cost a considerable amount of money), and that the therapy will no longer be effective after a certain period.
3. Increased anxiety: Another potential complication of DBS for OCD is that it may cause increased anxiety. This is because patients may feel apprehensive about their devices and uncertain about what kind of impact they are having on their mental health.
4. Inability to discontinue therapy: Finally, patients may find it difficult to discontinue DBS for OCD if it is not working well. This is because many people with OCD are dependent on the therapy and may become very upset if it is discontinued abruptly.
What Are The Next Steps After Deciding To Have DBS For OCD?

If you have decided to have DBS for OCD, here are the next steps:
1. Contact your doctor to schedule an appointment.
One of the first things you will need to do is schedule an appointment with your doctor. This is important so that they can evaluate whether or not DBS is right for you and can provide you with the necessary instructions and support.
2. Discuss your options with your doctor.
Your doctor will help you decide which type of DBS therapy is best for you and will provide you with all of the necessary information and support. They will also be able to answer any questions you may have about the treatment.
3. Begin your treatment.
Once you have had a consultation with your doctor, it is time to begin your DBS therapy. During this process, electrodes will be implanted into specific areas of your brain to ease your symptoms. It may take some time for the therapy to start working, but once it does, you will begin to see a significant decrease in your symptoms.
4. Commit yourself
Start living a better life with OCD by following your treatment plan and working towards your goals. Also, remember to keep up with your doctor’s appointments and keep up with therapy. If you do this, you will be able to overcome OCD and live a healthier life.
Conclusion
If you or someone you know is struggling with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), DBT may be an option for treatment. While there are many options available for treatment, and each person’s experience with DBT will be different, I hope this article has helped give you a little more information about what DBT is and how it might help alleviate your symptoms. If you still have questions after reading it, feel free to reach out to one of our team members at MantraCare.
For more information and guidance, please contact OCDMantra. OCD is a mental health disorder characterized by obsessions and compulsions. If you have any queries regarding OCD treatment, ERP therapy experienced therapists at OCDMantra can help: Book a trial OD therapy session.